Introduction:
Thai Baht is the official currency of Thailand, a very popular tourist destination that attracts a large number of tourists from around the world including India. Hence, the relationship between THB and INR rate has been pretty interesting, yet complex.
Another factor contributing to the popularity of the THB to INR exchange rate is the trade and investment activities between Thailand and India. These two countries have pretty strong economic connections leading to a continuous demand for both Thai Baht and Indian Rupees.
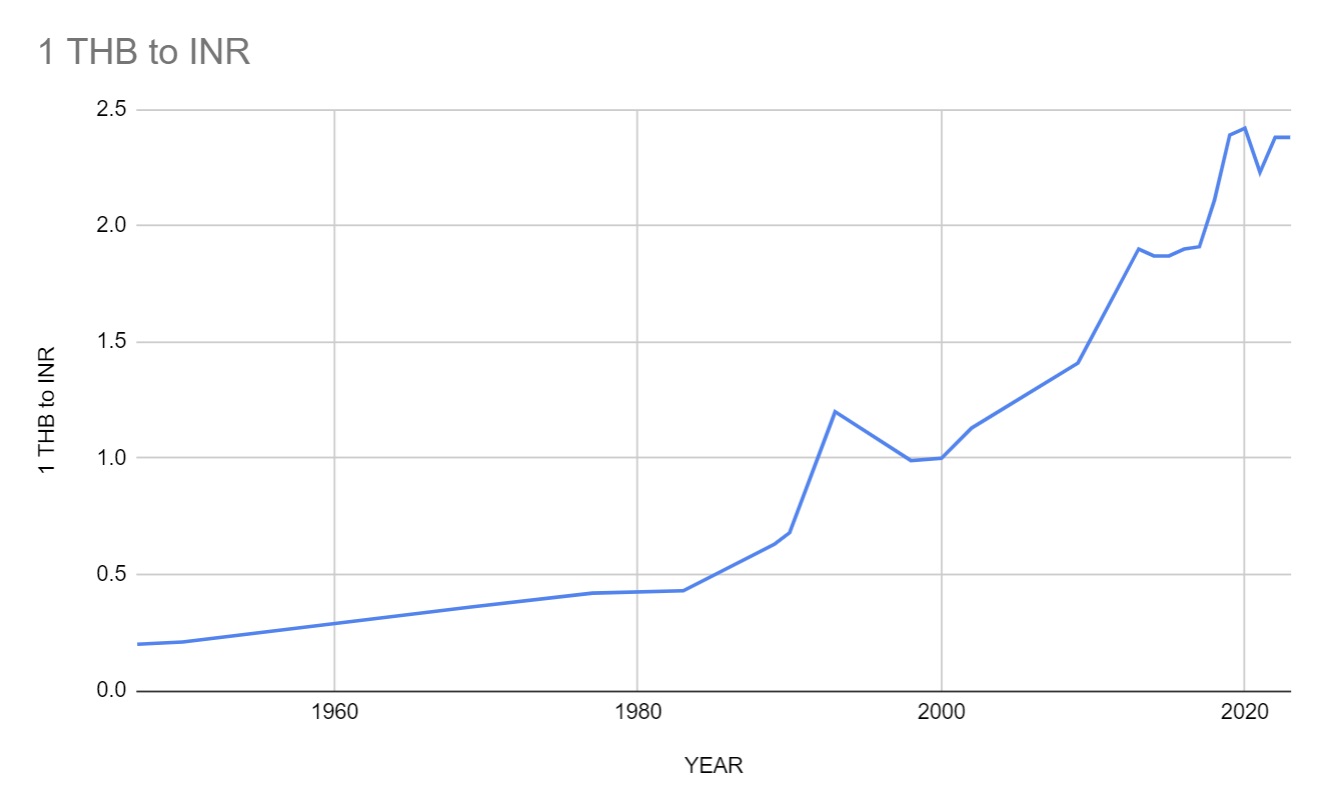
Value of 1 THB to INR from 1947 till today
| YEAR | 1 THB to INR | YEAR | 1 THB to INR |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1947 | 0.20 | 2014 | 1.87 |
| 1950 | 0.21 | 2015 | 1.87 |
| 1969 | 0.36 | 2016 | 1.90 |
| 1977 | 0.42 | 2017 | 1.91 |
| 1983 | 0.43 | 2018 | 2.11 |
| 1989 | 0.63 | 2019 | 2.39 |
| 1990 | 0.68 | 2020 | 2.42 |
| 1993 | 1.20 | 2021 | 2.23 |
| 1998 | 0.99 | 2022 | 2.38 |
| 2000 | 1.00 | 2023 | 2.38 |
| 2002 | 1.13 | 2024 | 2.37 |
| 2009 | 1.41 | 2025 | 2.58 |
| 2013 | 1.90 |
Historical Events That Noticeably Impacted THB to INR Rate
The value of the Thai Baht (THB) and the Indian rupee (INR) has been greatly impacted by a number of events, throughout time. Some of the most notable events are as follows:
1. Thai Baht Devaluation (1966)
The devaluation of the Thai baht, in 1966 was a key event of the past that had an impact on the exchange rate between THB and INR. Several factors contributed to this devaluation, including a growing trade deficit and high inflation. Thailand was facing an increasing trade deficit meaning that it was importing goods and services than it was exporting.
As a result, it put downward pressure on the value of the Thai baht. Additionally, Thailand experienced levels of inflation. This resulted in prices for Thai goods and services making them less competitive, in the market. Consequently, exports declined, further worsening the trade deficit and putting pressure on the value of the Thai baht.
2. The Plaza Accord (1985)
The value of the US dollar dropped against other currencies, as a result of the Plaza Accord. This was helpful for Thailand as it improved the worldwide competitiveness of Thai exports and the consumer appeal of Thai goods and services. It benefited the Thai economy by accelerating employment growth and economic expansion. As a result, there was a rise in the value of Thai baht (THB) relative to the Indian rupee (INR).
3. Thai Reforms (1992)
The Thai government implemented a number of key economic reforms back in 1992. These led to opening new doors for their finance industry and removing trade prohibitions which caused a remarkable period of fast economic growth. Their economy boomed from 1992 to 1996, expanding at an astounding average annual rate of 8.2%.
And as a result? The exchange rate between the Thai baht and the Indian rupee was subject to impact because of Thailand’s economic boom. Thailand’s currency appreciated against INR in value as a result of its economic development.
4. Asian Financial Crisis (1997)
The Asian financial crisis of 1997, often referred to as the “Asian Economic Storm,” swept across the Asian region, leaving a trail of economic crisis. Thailand was one of the worst-hit countries and experienced a sharp depreciation of the Thai Baht against other currencies including INR. In July 1997, the Thai government was faced with a shortage of foreign exchange reserves and hence was forced to float freely, losing over 50% of its value against other currencies.
5. Global Financial Crisis (2008)
The bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers set off a global financial crisis that also impacted the THB to INR exchange rate. Due to the global economic downturn, lack of investor confidence, and capital outflow from emerging nations, both currencies were deeply affected, however, when compared, the rupee depreciated more against other currencies including THB as well. This was because India had a greater reliance on foreign investment at the time and had a more exposed financial sector.
6. Thai Stimulus Package (2009)
The Thai government unveiled a comprehensive stimulus plan that covered a range of measures like tax reductions, infrastructure investments, and company loan extensions. This package ended up being a success, helping Thailand briefly appreciate against other currencies including INR.
The reason for only brief appreciation is that there is another side to this story. For the stimulus package’s success, the Thai government had to borrow money and raise spending to pay for all of these policies. This therefore gave the Thai baht a certain downward pressure as well.
7. Thai Baht Appreciation (2011)
Something intriguing happened to the currencies in India and Thailand in 2011. The Thai baht strengthened against the Indian rupee. Why did this occur, you ask? Well, a few things were happening.
First, political conditions in India were not exactly ideal. Investors became somewhat uneasy because of the numerous differences and uncertainty in the nation’s leadership which led to investors withdrawing money and ultimately the Indian rupee losing value against other currencies including THB.
Thailand’s economic performance in 2011 was, on the other hand, very strong. Foreign investors regarded the nation as a fantastic destination to invest in because its firms were expanding. Therefore, there was an increase in the amount of money entering Thailand, which was commendable for the Thai baht and it appreciated against the INR.
8. India’s Economic Recovery (2014-2016)
With Narendra Modi’s government coming into power in 2014, economic reforms such as the ‘Make in India’ initiative and improved investor confidence helped stabilize the Rupee. In contrast, Thailand’s economy faced some political uncertainty due to the military coup in 2014, but strong tourism revenues prevented a major decline in the Baht.
9. Rising Oil Prices and India’s Trade Deficit (2018)
Global crude oil prices surged in 2018, increasing India’s import bill and widening the current account deficit. As India is heavily dependent on oil imports, this puts pressure on the Rupee. Simultaneously, Thailand maintained a current account surplus, strengthening the Baht against the INR.
10. Thailand’s Booming Tourism (2019)
The Thai Baht continued to appreciate in 2019, reaching one of its strongest levels against the Indian Rupee. The reasons included Thailand’s booming tourism industry. India’s economic slowdown, with GDP growth falling to a six-year low due to weak consumption and the shadow banking crisis. As a result, the Thai Baht strengthened significantly against the Indian Rupee.
11. COVID-19 Impact (2020)
The pandemic led to massive economic disruptions. India faced a sharp contraction in GDP, and the INR depreciated due to reduced foreign investment and economic uncertainty. Thailand’s tourism-dependent economy was hit hard, but the Baht remained relatively stable because of strong foreign reserves and low external debt.
12. Global Inflation and Stabilization (2022-2023)
The world experienced rising inflation and aggressive interest rate hikes by central banks, including the US Federal Reserve and RBI. While this created short-term volatility, both India and Thailand adopted it, leading to a relatively stable THB-INR exchange rate.
13. A Potential Shift in Currency Dynamics
A significant rise in THB to INR in 2025 suggests Thailand’s economic resurgence (stronger GDP growth, rising foreign investment) or India’s facing inflationary pressures and currency depreciation. This could be driven by shifts in global trade, foreign investment, or central bank policies.
Key Factors That Influence THB to INR Exchange Rate
The Thai baht (THB) and Indian rupee (INR) have a complex relationship that is impacted by many different factors. These factors consist of:
1. Economic Situation: The THB to INR exchange rate is influenced by the relative economic performance of Thailand and India. The THB rises against the INR when Thailand’s economy grows faster than India’s. On the other hand, the INR gains value relative to the THB if India’s economy is expanding more quickly.
2. Interest Rates: THB gains value vs INR as a result of Thailand’s higher interest rates relative to India. This is due to the possibility of investors receiving higher returns on their investments in Thailand. In contrast, the INR tends to gain value versus the THB if India’s interest rates exceed Thailand’s.
3. Inflation: The currency rate can also be affected by inflation. The buying power of THB is diminished due to Thailand’s greater inflation rate than India’s, which results in a decline in value relative to INR. In contrast, the INR tends to weaken against the THB when India has more inflation.
4. Flows of Trade and Investment: The ratio of trade to investment between the two nations must be balanced. The THB appreciates versus the INR if Thailand exports more to India than India exports to Thailand. In contrast, if India increases its exports to Thailand, the INR appreciates versus the THB.
5. Investor Risk Appetite: If investors believe Thailand to be riskier than India, they may select more stable political and economic systems, which might cause the THB to decline versus the INR. On the other hand, risk-taking investors could pick developing countries like Thailand, which would cause the THB to increase.
1 USD to INR from 1947 to 2025: Historical Exchange Rates Explained
1 AED to INR from 2008 to 2025, Historical Exchange Rates Explained
1 CAD to INR from 1947 to 2025, Historical Exchange Rates Explained
1 EUR to INR from 1990 to 2025, Historical Exchange Rates Explained
1 AUD to INR from 1966 till now, Historical Exchange Rates Explained
1 INR to PKR from 1947 to 2025, Historical Exchange Rates Trend Explained
1 GBP to INR from 1947 to 2025: Historical Exchange Rates Explained